本项目旨在构建一个本地智能舆情分析系统,通过自然语言处理与多工具写作,实现用户查询意图的自动理解、新闻检索、情绪分析、结构化输出与邮件推送。
具体执行流程依次为:用户查询,提取关键词,调用api搜索,获取新闻前5篇文章,分析情感倾向,保存为md文件,发送邮件。
只考虑MCP服务器部署在本地,项目使用python语言编写,版本为3.12。
项目链接:JLQusername/make-a-simple-mcp-server: 本项目旨在构建一个本地智能舆情分析系统,通过自然语言处理与多工具写作,实现用户查询意图的自动理解、新闻检索、情绪分析、结构化输出与邮件推送。 (github.com)
项目初始化 首先安装uv,执行pip install uv,可以通过uv --version和uvx --version来检测环境是否安装成功。
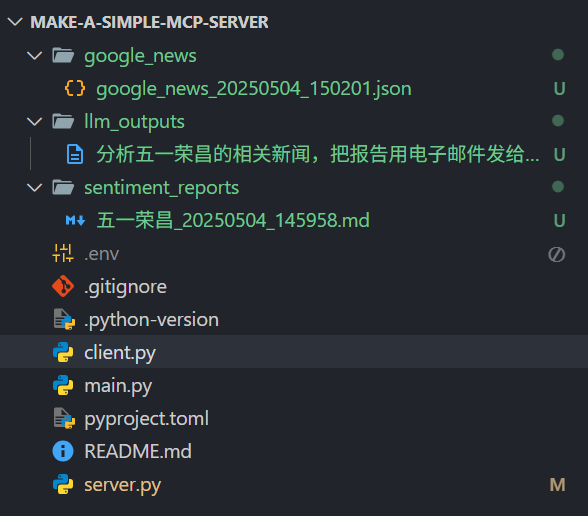
执行uv init 项目名称,则会在当前目录下创建一个文件夹,文件夹名称为输入的项目名称。
这个文件夹下的文件如下:
然后我们手动创建三个文件:client.py、server.py、.env,接下来会主要对client.py和server.py进行编写。
环境参数 需要去阿里百炼平台申请一个key,然后在.env文件中加入:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 BASE_URL="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1"
client.py 首先引入必要的库:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import asyncioimport osimport jsonfrom typing import Optional , List from contextlib import AsyncExitStackfrom datetime import datetimeimport refrom openai import OpenAIfrom dotenv import load_dotenvfrom mcp import ClientSession, StdioServerParametersfrom mcp.client.stdio import stdio_client
加载.env环境变量:
客户端初始化 建立一个MCPClient类,进行初始化:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class MCPClient :def __init__ (self ):self .exit_stack = AsyncExitStack()self .api_key = os.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY" )self .base_url = os.getenv("BASE_URL" )self .model = os.getenv("MODEL" )if not self .api_key:raise ValueError("❌ DASHSCOPE_API_KEY is not set,请在.env文件中设置" )if not self .base_url:raise ValueError("❌ BASE_URL is not set,请在.env文件中设置" )if not self .model:raise ValueError("❌ MODEL is not set,请在.env文件中设置" )self .client = OpenAI(api_key=self .api_key, base_url=self .base_url)self .session: Optional [ClientSession] = None
建立连接 客户端初始化后,要与服务端建立连接,在MCPClient中写一个与服务器建立连接的函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 async def connect_to_server (self, server_script_path: str ):"""连接到服务器 完成初始化阶段""" ".py" )".js" )if not (is_py or is_js):raise ValueError("❌ 服务器脚本类型错误,请使用.py或.js文件" )"python" , server_script_path if is_py else "node" None await self .exit_stack.enter_async_context(self .stdio, self .writer = stdio_transportself .session = await self .exit_stack.enter_async_context(self .stdio, self .writer)await self .session.initialize()await self .list_tools()async def list_tools (self ):"""请求可用工具列表""" await self .session.list_tools()self .tools = ["type" : "function" ,"function" : {"name" : tool.name,"description" : tool.description,"input_schema" : tool.inputSchema,for tool in response.toolsprint (f"已连接到服务器,🔧 工具列表: {self.tools} " )
处理用户查询 想要把结果输出到文件中,就要写确定输出路径的函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 def clean_filename (self, text: str ) -> str :"""清理文本,生成合法的文件名""" r"[\\/:*?\"<>|]" , "" , text)return text[:50 ]def prepare_file_paths (self, query: str ) -> tuple [str , str , str , str ]:"""准备文件路径相关信息""" self .clean_filename(query)"%Y%m%d_%H%M%S" )r"(关于|分析|查询|搜索|查看)([^的\s,。、?\n]+)" , query2 ) if keyword_match else "分析对象" r'[\\/:*?"<>|]' , "" , keyword)[:20 ]f"{safe_keyword} _{timestamp} .md" "./sentiment_reports" , exist_ok=True )"./sentiment_reports" , md_filename)f"{safe_filename} _{timestamp} .txt" "./llm_outputs" , exist_ok=True )"./llm_outputs" , txt_filename)return md_filename, md_path, txt_filename, txt_path
然后我们需要获取计划执行的工具列表:
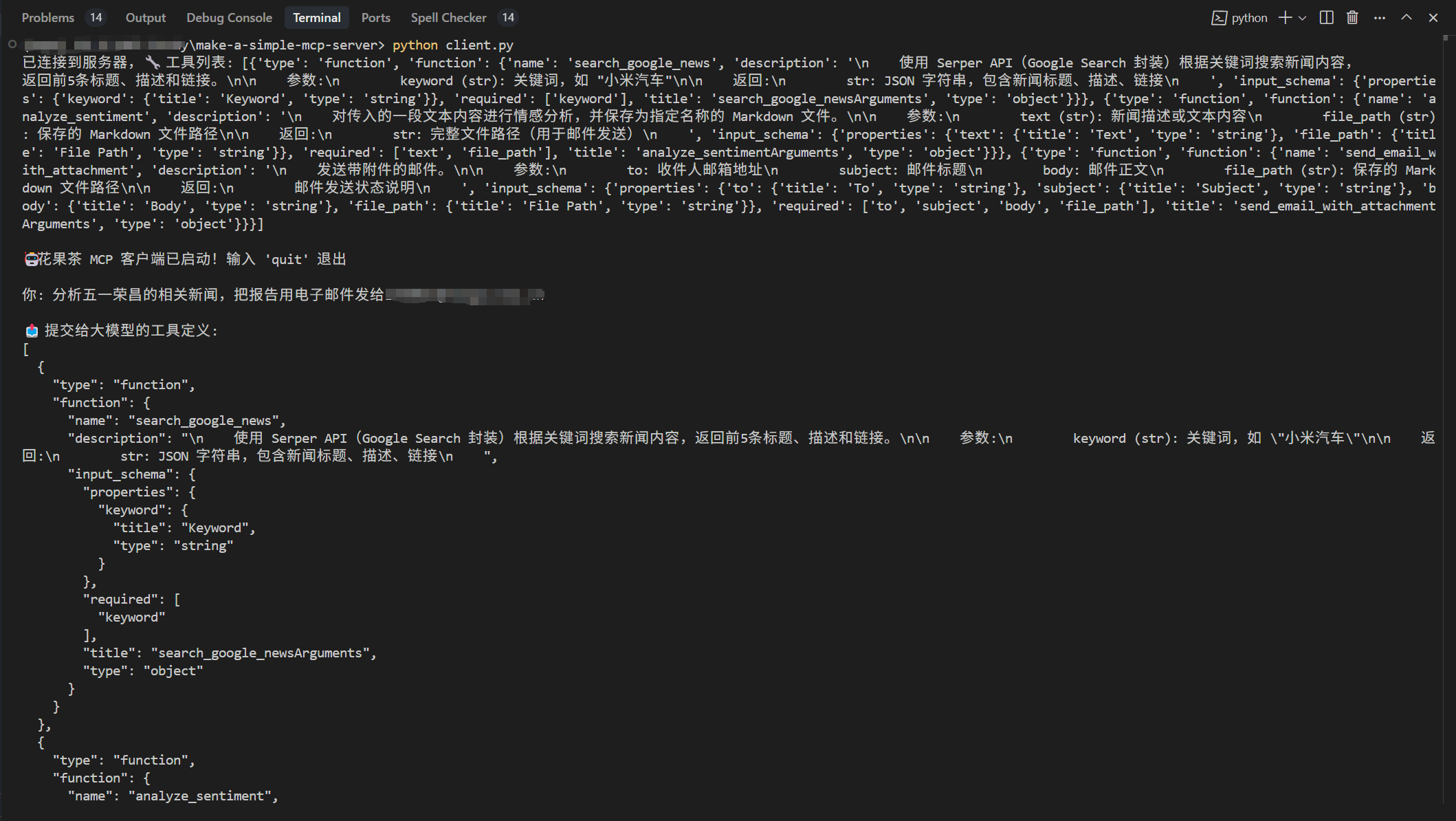
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 async def plan_tool_usage (self, query: str , tools: List [dict ] ) -> List [dict ]:"""获取计划执行的工具列表""" print ("\n📤 提交给大模型的工具定义:" )print (json.dumps(tools, ensure_ascii=False , indent=2 ))"\n" .join(f"- {tool['function' ]['name' ]} : {tool['function' ]['description' ]} " for tool in tools"role" : "system" ,"content" : ("你是一个智能任务规划助手,用户会给出一句自然语言请求。\n" "你只能从以下工具中选择(严格使用工具名称):\n" f"{tool_list_text} \n" "如果多个工具需要串联,后续步骤中可以使用 {{上一步工具名}} 占位。\n" "返回格式:JSON 数组,每个对象包含 name 和 arguments 字段。\n" "不要返回自然语言,不要使用未列出的工具名。" "role" : "user" , "content" : query}]self .client.chat.completions.create(self .model,"none" ,True ,"" for chunk in response:if hasattr (chunk, "choices" ) and chunk.choices:0 ].deltaif hasattr (delta, "content" ) and delta.content:match = re.search(r"```(?:json)?\s*([\s\S]+?)\s*```" , content)if match :match .group(1 )else :r"/\*[\s\S]*?\*/" , "" , json_text)r"//.*" , "" , json_text)print (f"🟡 解析前的内容: {repr (json_text)} " )try :return plan if isinstance (plan, list ) else []except Exception as e:print (f"❌ 获取计划执行的工具列表失败: {e} \n原始返回: {json_text} " )return []
然后依次进行执行工具列表里的工具:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 async def execute_tool_chain ( self, query: str , tool_plan: list , md_path: str list :"""执行工具调用链""" "role" : "user" , "content" : query}]for step in tool_plan:"name" ]"arguments" ]self .resolve_tool_args(tool_name, tool_args, tool_outputs, md_path)await self .session.call_tool(tool_name, tool_args)0 ].text"role" : "assistant" ,"tool_call_id" : tool_name,"content" : result.content[0 ].text,print (f"🔧 执行工具: {tool_name} ,参数: {tool_args} " )print (f"🔧 工具输出: {result.content[0 ].text} " )return messagesdef resolve_tool_args ( self, tool_name: str , tool_args: dict , tool_outputs: dict , md_filename: str , md_path: str , for key, val in tool_args.items():if isinstance (val, str ) and val.startswith("{{" ) and val.endswith("}}" ):"{} " )if tool_name == "analyze_sentiment" and "file_path" not in tool_args:"file_path" ] = md_pathif ("send_email_with_attachment" and "attachment_path" not in tool_args"attachment_path" ] = md_path
可以考虑把最终的对话记录保存一下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 async def generate_final_response (self, messages: list ) -> str :"""生成最终响应""" self .client.chat.completions.create(self .model,True ,"" for chunk in response:if hasattr (chunk, "choices" ) and chunk.choices:0 ].deltaif hasattr (delta, "content" ) and delta.content:return final_outputdef save_conversation (self, query: str , final_output: str , file_path: str ):"""保存对话记录""" with open (file_path, "w" , encoding="utf-8" ) as f:f"🤵 用户提问:{query} \n\n" )f"🤖 模型回复:\n{final_output} \n" )print (f"📄 对话记录已保存为:{file_path} " )
整合成处理用户查询的主流程的函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 async def process_query (self, query: str ) -> str :"""处理用户查询的主流程""" self .prepare_file_paths(query)f" [md_filename={md_filename} ] [md_path={md_path} ]" await self .plan_tool_usage(query, self .tools)await self .execute_tool_chain(query, tool_plan, md_filename, md_path)await self .generate_final_response(messages)self .save_conversation(query, final_output, txt_path)return final_output
对话入口 想要和LLM进行对话,必须得有个入口:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 async def chat_loop (self ):print ("\n🤖花果茶 MCP 客户端已启动!输入 'quit' 退出" )while True :try :input ("\n你: " ).strip()if query.lower() == "quit" :break await self .process_query(query)print (f"\n🤖 AI: {response} " )except Exception as e:print (f"\n⚠️ 发生错误: {str (e)} " )
连接关闭 任务执行结束后,为了防止浪费连接资源,需要对其进行关闭
1 2 async def cleanup (self ):await self .exit_stack.aclose()
执行入口 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 async def main ():"server.py" try :await client.connect_to_server(server_script_path)await client.chat_loop()finally :await client.cleanup()if __name__ == "__main__" :
server.py 对于server.py,第一步也是引入必要的库,并加载环境变量:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import osimport jsonimport smtplibfrom datetime import datetimefrom email.message import EmailMessageimport httpxfrom mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCPfrom dotenv import load_dotenvfrom openai import OpenAI
还需要初始化MCP服务器:
1 mcp = FastMCP("NewsServer" )
获取新闻的工具 首先要使用装饰器@mcp.tool,这可以把函数注册为工具
1 2 @mcp.tool async def search_google_news (keyword: str ) -> str :
新闻来源于https://google.serper.dev/news,我们需要对应的api,可以直接从环境变量中获取:
1 2 3 4 "SERPER_API_KEY" )if not api_key:raise ValueError("❌ SERPER_API_KEY is not set,请在.env文件中设置" )
然后写一个发请求获取新闻的函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 async def fetch_news_data (api_key: str , keyword: str ) -> dict :"""发送新闻搜索请求并获取结果""" "https://google.serper.dev/news" "X-API-KEY" : api_key, "Content-Type" : "application/json" }"q" : keyword}async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:await client.post(url, headers=headers, json=payload)if "news" not in data:raise ValueError("❌ 未获取到搜索结果" )return data["news" ]
然后对新闻进行保存:
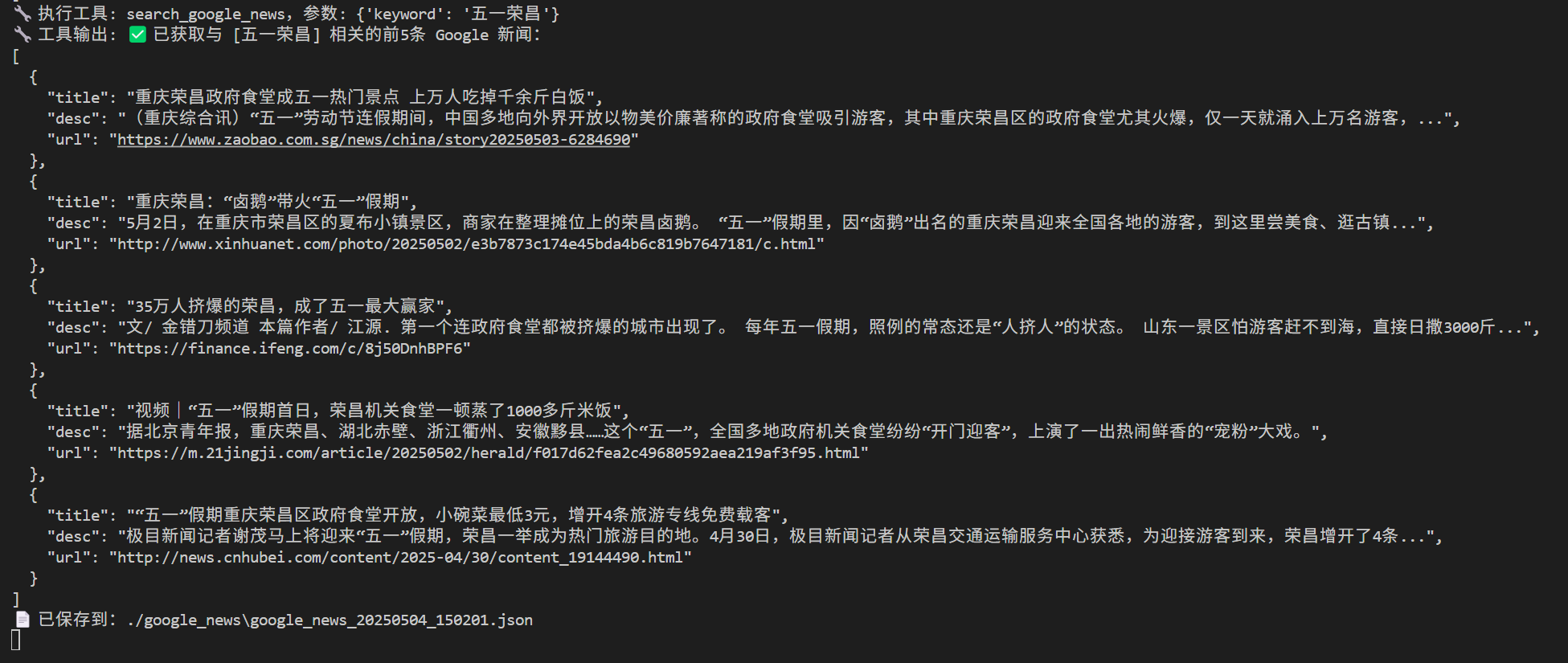
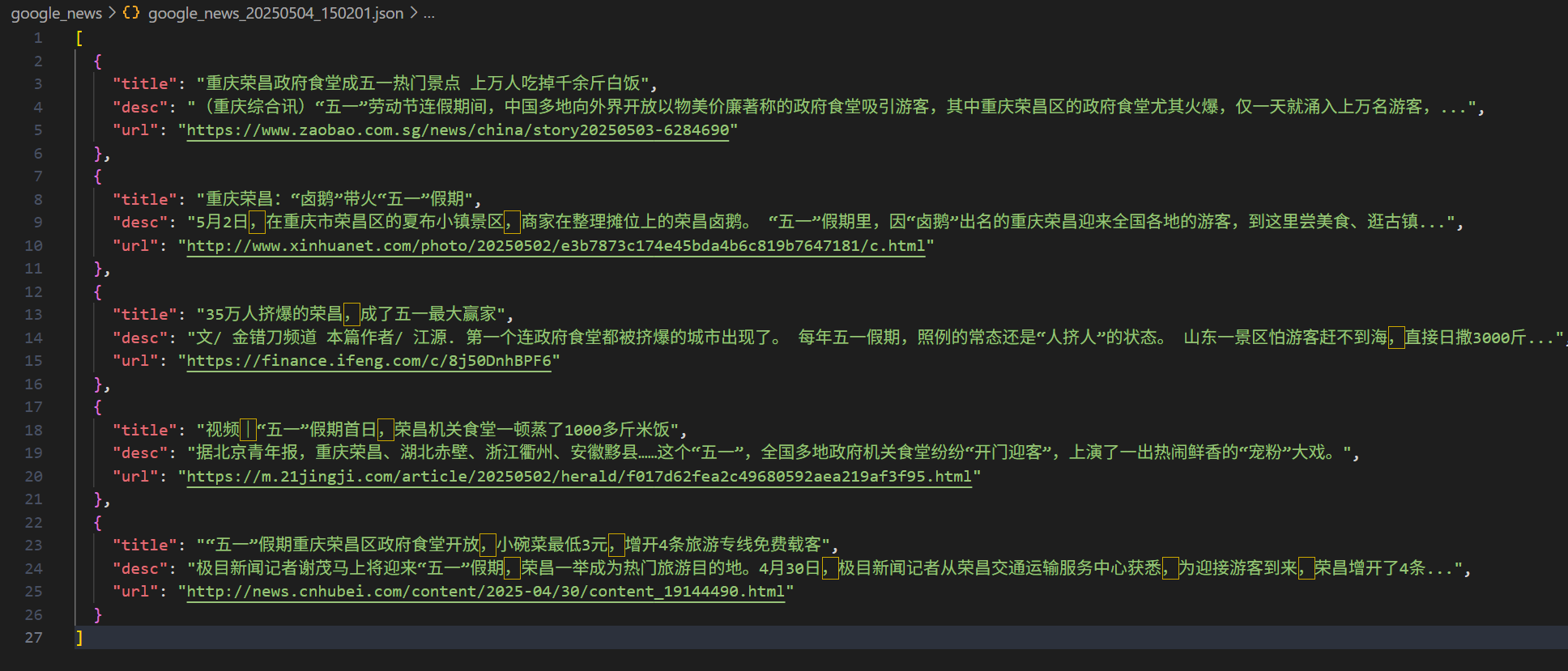
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 def save_news_to_file (articles: list ) -> str :"""将新闻结果以带有时间戳命名后的 JSON 格式文件的形式保存在本地指定的路径""" "./google_news" True )f"google_news_{datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d_%H%M%S' )} .json" with open (file_path, "w" , encoding="utf-8" ) as f:False , indent=2 )return file_path
完整的search_google_news工具如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 @mcp.tool async def search_google_news (keyword: str ) -> str :""" 使用 Serper API(Google Search 封装)根据关键词搜索新闻内容,返回前5条标题、描述和链接。 参数: keyword (str): 关键词,如 "小米汽车" 返回: str: JSON 字符串,包含新闻标题、描述、链接 """ "SERPER_API_KEY" )if not api_key:raise ValueError("❌ SERPER_API_KEY is not set,请在.env文件中设置" )await fetch_news_data(api_key, keyword)"title" : item.get("title" ),"desc" : item.get("snippet" ),"url" : item.get("link" ),for item in news_data[:5 ]return (f"✅ 已获取与 [{keyword} ] 相关的前5条 Google 新闻:\n" f"{json.dumps(articles, ensure_ascii=False , indent=2 )} \n" f"📄 已保存到:{file_path} "
情感分析报告生成工具 先写一个报告格式的函数:
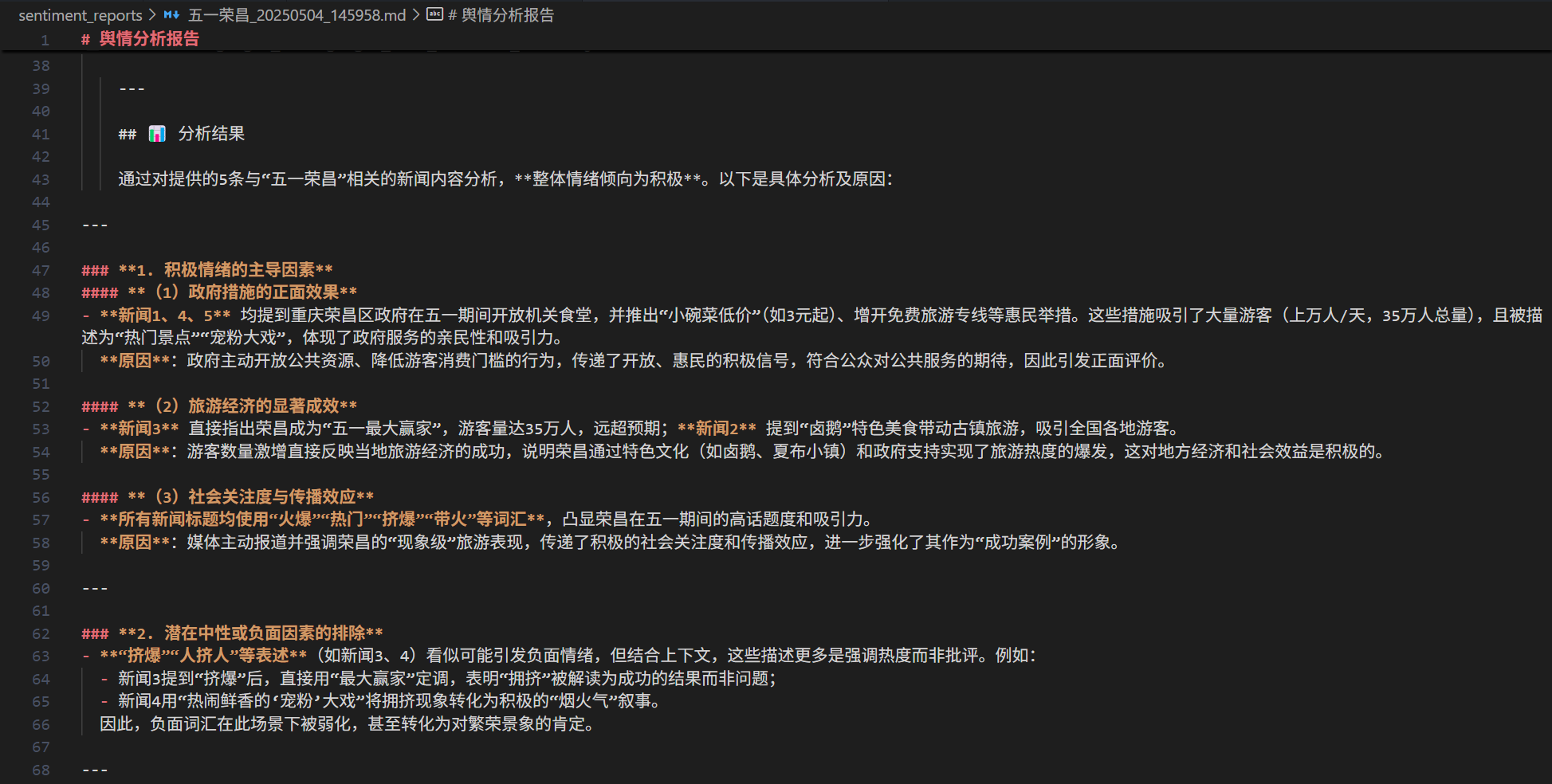
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 def generate_sentiment_report (text: str , result: str ) -> str :return f"""# 舆情分析报告 **分析时间:** {datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S' )} --- ## 📥 原始文本 {text} --- ## 📊 分析结果 {result} """
然后可以写出情感分析报告生成工具:
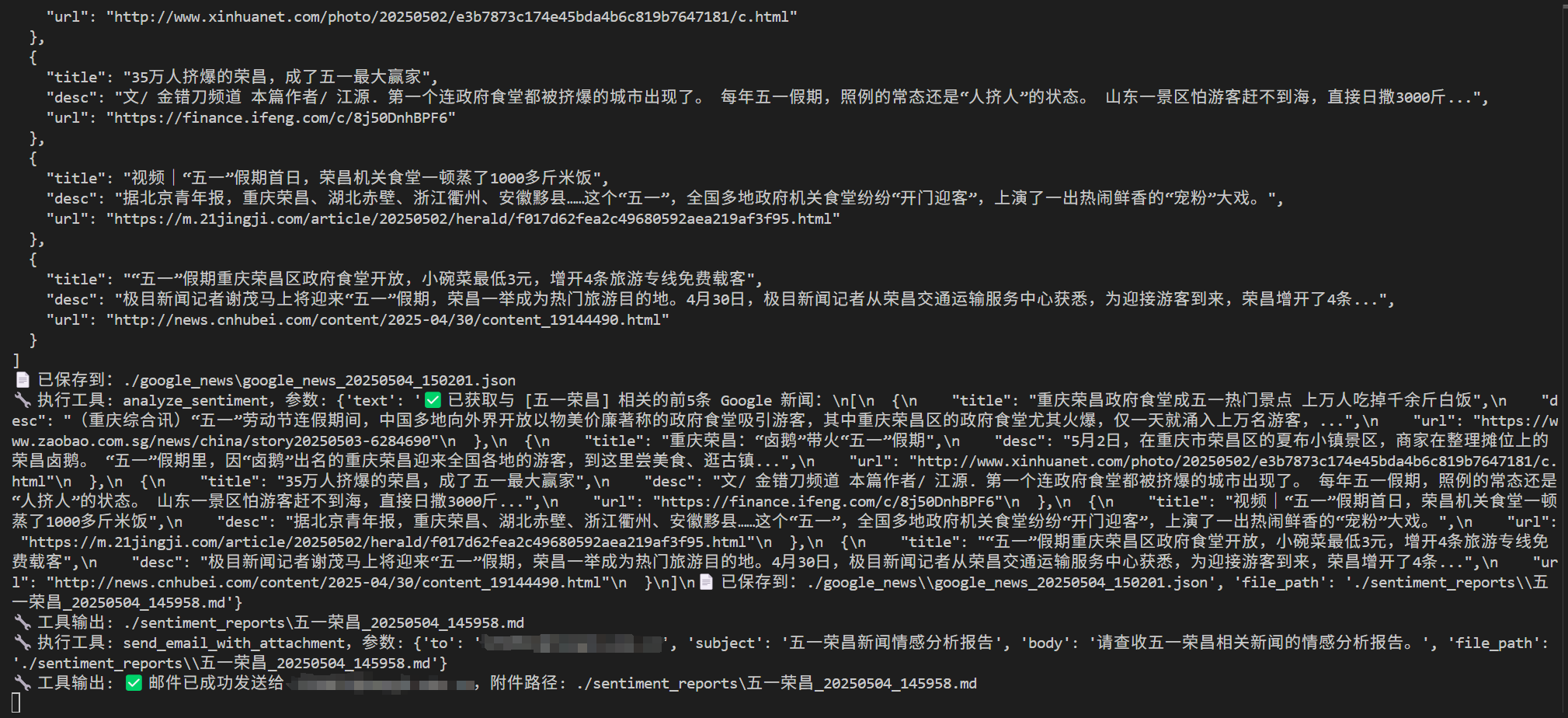
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 @mcp.tool() async def analyze_sentiment (text: str , file_path: str ) -> str :""" 对传入的一段文本内容进行情感分析,并保存为指定名称的 Markdown 文件。 参数: text (str): 新闻描述或文本内容 file_path (str): 保存的 Markdown 文件路径 返回: str: 完整文件路径(用于邮件发送) """ "DASHSCOPE_API_KEY" )"BASE_URL" )"MODEL" )if not api_key:raise ValueError("❌ DASHSCOPE_API_KEY is not set,请在.env文件中设置" )if not base_url:raise ValueError("❌ BASE_URL is not set,请在.env文件中设置" )if not model:raise ValueError("❌ MODEL is not set,请在.env文件中设置" )f"请对以下新闻内容进行情绪倾向分析,并说明原因:\n\n{text} " "role" : "user" , "content" : prompt}], stream=True "" for chunk in response:if hasattr (chunk, "choices" ) and chunk.choices:0 ].deltaif hasattr (delta, "content" ) and delta.content:with open (file_path, "w" , encoding="utf-8" ) as f:return file_path
发送邮件工具 这里需要拿到邮件的smtp_server、smtp_port、sender_email、sender_pass等信息
增加附件函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 def add_attachment_to_email (msg: EmailMessage, file_path: str ):"""添加附件并发送邮件""" try :with open (file_path, "rb" ) as f:"application" ,"octet-stream" ,"" ,"filename*" : encode_rfc2231(file_name, "utf-8" )},except Exception as e:return f"❌ 附件读取失败: {str (e)} "
发送邮件函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 def send_email ( msg: EmailMessage, to: str , smtp_server: str , smtp_port: int , sender_email: str , sender_pass: str , file_path: str , """发送邮件""" try :with smtplib.SMTP_SSL(smtp_server, smtp_port) as server:return f"✅ 邮件已成功发送给 {to} ,附件路径: {file_path} " except Exception as e:return f"❌ 邮件发送失败: {str (e)} "
这里的smtp_server、smtp_port、sender_email、sender_pass是我们在环境变量中设置的,需要进行读取
然后创建邮件,填写内容,再添加附件,进行发送,就完成了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 @mcp.tool() async def send_email_with_attachment ( to: str , subject: str , body: str , file_path: str str :""" 发送带附件的邮件。 参数: to: 收件人邮箱地址 subject: 邮件标题 body: 邮件正文 file_path (str): 保存的 Markdown 文件路径 返回: 邮件发送状态说明 """ "SMTP_SERVER" )int (os.getenv("SMTP_PORT" , 465 ))"EMAIL_USER" )"EMAIL_PASS" )if not smtp_server:raise ValueError("❌ SMTP_SERVER is not set,请在.env文件中设置" )if not sender_email:raise ValueError("❌ EMAIL_USER is not set,请在.env文件中设置" )if not sender_pass:raise ValueError("❌ EMAIL_PASS is not set,请在.env文件中设置" )if not os.path.exists(file_path):raise ValueError(f"❌ 附件路径无效,未找到文件: {file_path} " )"Subject" ] = str (Header(subject, "utf-8" ))"From" ] = str (Header(sender_email, "utf-8" ))"To" ] = str (Header(to, "utf-8" ))"utf-8" )return send_email(
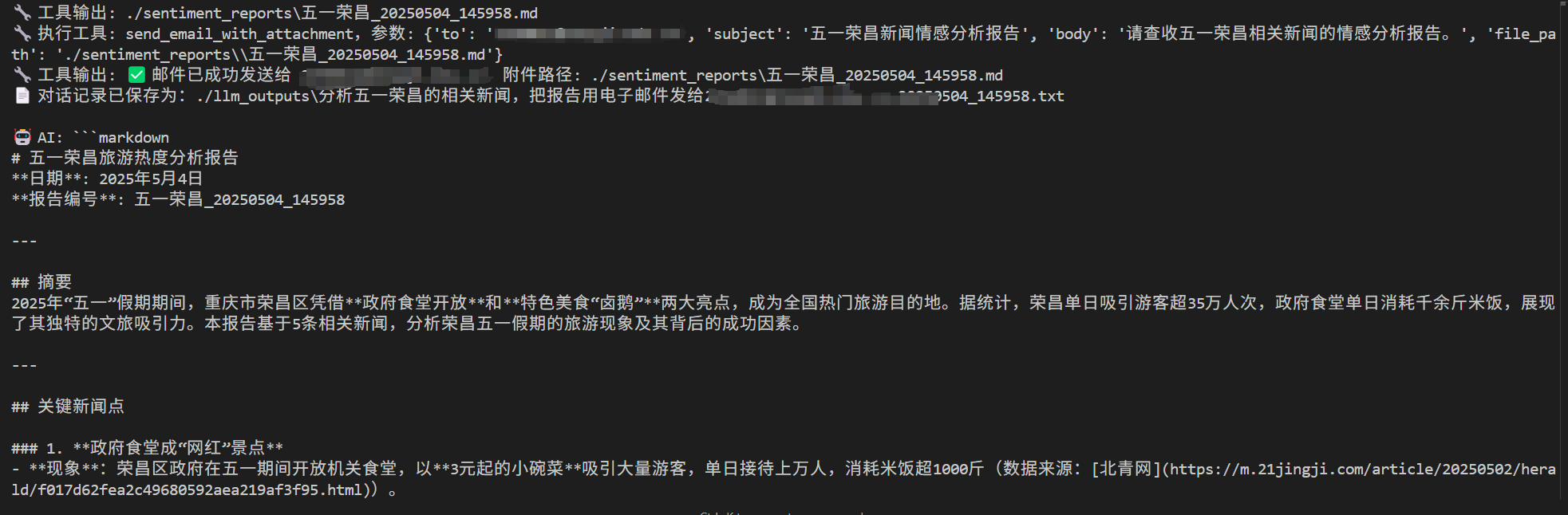
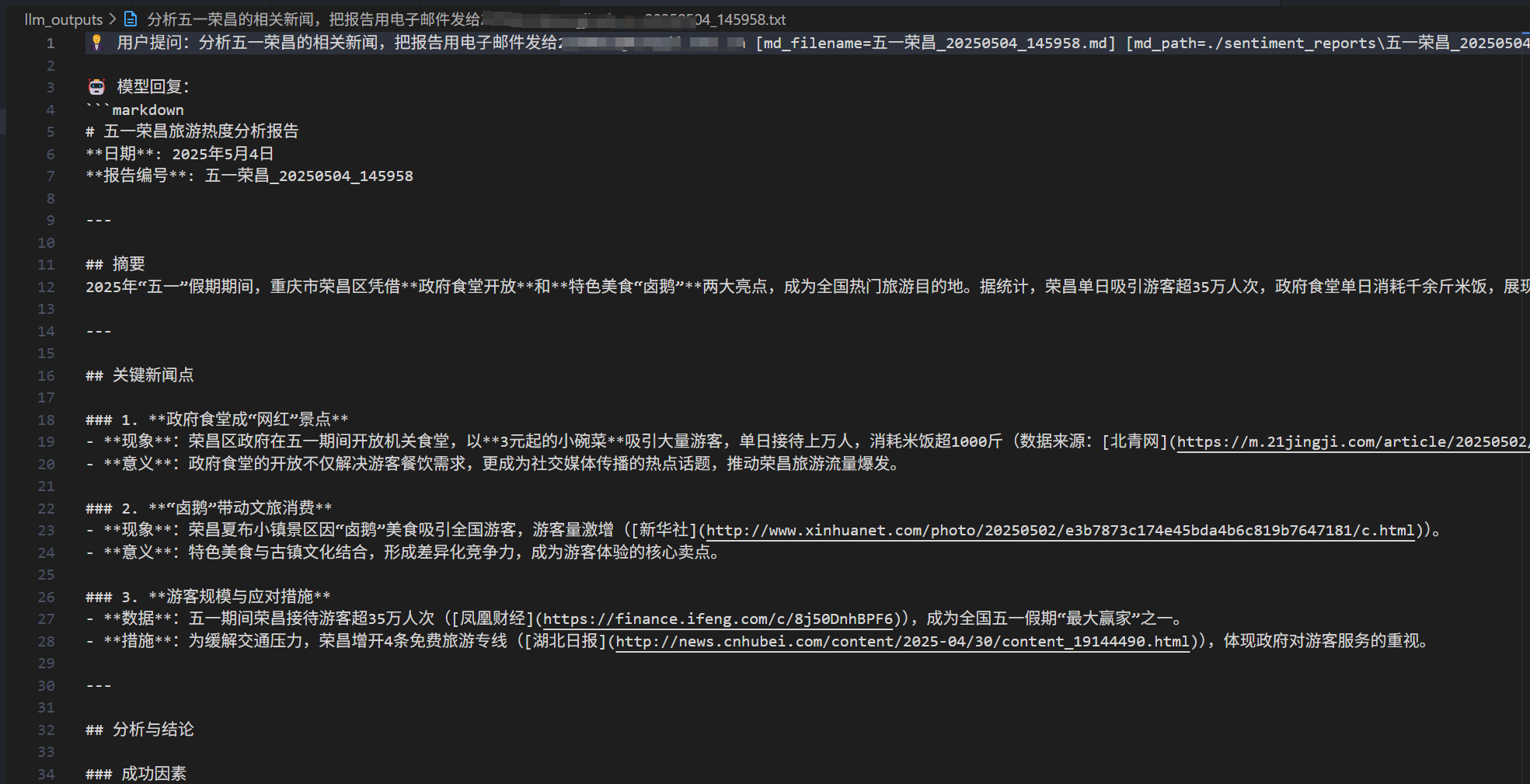
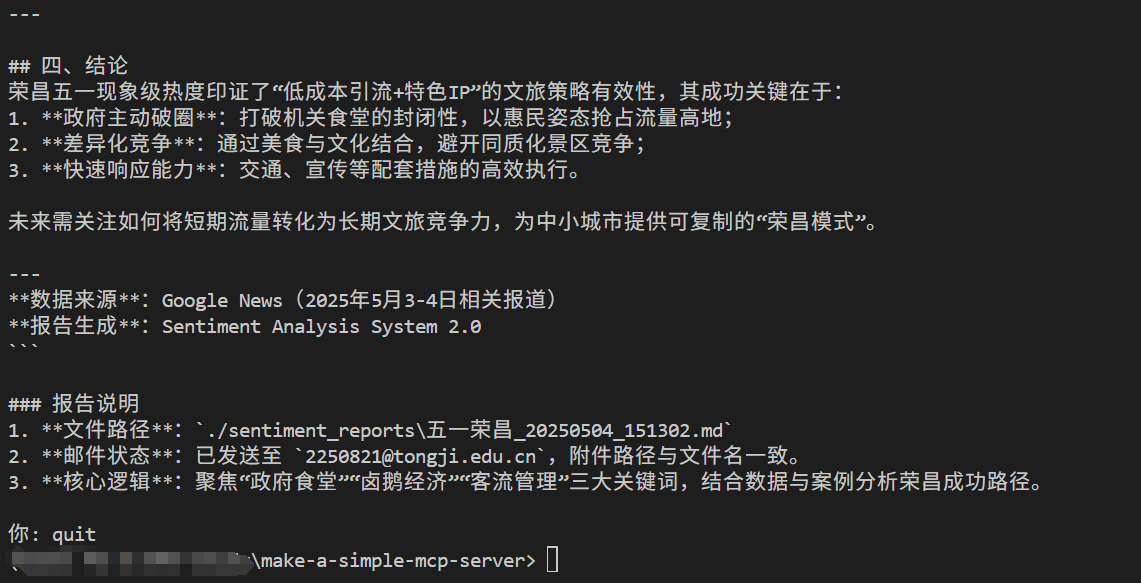
测试运行 运行client.py:
可以看到,对应的文件也被保存了
输入quit就可以结束对话